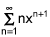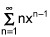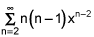Mark M. answered • 04/15/21
Retired math prof. Calc 1, 2 and AP Calculus tutoring experience.
If f(x) = 1 / (1-x), then f'(x) = 1 / (1-x)2 and f"(x) = 2 / (1-x)3
The Maclaurin Series for 1 / (1-x) is ∑(n=0 to infinity) xn.
Differentiate twice to get the Maclaurin Series for 2 / (1-x)3.
I think that you'll get ∑(n=2 to infinity) n(n-1)xn-2.


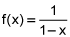 , find the power series for
, find the power series for 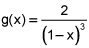 .
.