Tom K. answered • 03/28/21
Knowledgeable and Friendly Math and Statistics Tutor
The integral is -1/(2 (ln(k))^2) + C; -1/(2 ln^2(k)) has a limit of 0 as x goes to infinity. Note the negative sign; this assures us that the integral will be positive.
Thus, the sum converges.


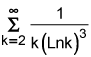 is convergent or divergent. Make sure that you set up the problem correctly and use the proper notation.
is convergent or divergent. Make sure that you set up the problem correctly and use the proper notation.

