J.R. S. answered • 11/12/19
Ph.D. University Professor with 10+ years Tutoring Experience
Let us find the Keq for this reaction:
H2(g) + F2(g) <==> 2HF(g)
Keq = [HF]2 / [H2][F2] = (0.409)2 / (0.0501)(0.0104)
Keq = 321
Adding 0.207 moles F2 to a 5.22 L container produces is equivalent to 0.207 mol / 5.22 L = 0.0397 M
Adding this to the equilibrium [F2] we get 0.0397 + 0.0104 = 0.0501 M
This will push the reaction to the right toward the product side (Le Chatelier)
H2(g) + F2(g) <==> 2HF(g)
0.0501... 0.0501.........0.409....Initial
-x.............. -x...............+2x........Change
0.0501-x....0.0501-x.....2x......Equilibrium
Keq = 321 = (0.0501-x)(0.0501-x) / 2x
The rest is algebra. Solve for x and subtract that value from 0.0501 to get the concentration of H2 and F2. Multiply the value of x by 2 to get the concentration of HF.


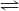 2 HF(
2 HF(


