J.R. S. answered • 02/10/19
Ph.D. University Professor with 10+ years Tutoring Experience
First, find Keq from the equilibrium concentrations provided.
Keq = [SO3][NO]/[SO2][NO2] = (3.00)(2.00)/(4.00)(0.500) = 3.00
Next, set up an ICE table reflecting conditions described:
SO2 + NO2 <===> SO3 + NO
4..........0.5................3............2.........I
-x........-x.................+x..........+x........C
4-x....0.5-x............3+x.........2+x.......E
Keq = 3.00 = (3+x)(2+x)/(4-x)(0.5-x)
Solve for x. I found it to be x = 1.7 (please do check my math. I'm better at chemistry than at math).
Assuming this is correct, then plug this in to the E in the table where NO = 2+x and that means that
new concentration of NO = 2 + 1.7 = 3.7 M
For part (b), take a similar approach but you will use the initial concentrations and the final equilibrium concentration of SO3 will be 4.20, meaning it increased by 1.20 M. Hopefully you can figure this out.


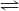 SO
SO


