Zeeshan S. answered • 07/06/23
Ace SAT/ACT, Math, Physics & Engineering with a Graduate Engineer
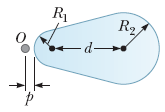
a. With light going through the piece of glass from left to right, the radius of the first surface is positive and that of the second surface is negative according to the sign convention. Thus, R1 = +2.00 cm and R2 = – 4.00 cm. Applying n1/p + n2/q = (n2 − n1)/R to the first surface gives 1.00/1.03 cm + 1.50/q1 = (1.50 − 1.00)/ + 2.00 cm which yields q1 = – 2.07 cm. The first surface forms a virtual image 2.07 cm to the left of that surface and 16.39 cm to the left of the second surface.
The image formed by the first surface is the object for the second surface, so p2 = +16.39 cm.
Applying n1/p + n2/q = (n2 − n1)/R to the second surface gives 1.5/16.39 cm + 1/q2 = (1.00 − 1.50)/ - 4.00 cm
Thus q2 = +29.87 cm to the right of the second surface
b. The final image distance is positive, so the image is real.