In this problem, T(t) will represent the temperature of the roast (in degrees Fahrenheit) after t hours. We can see from the given information that A = 20 and T(0) = 68. Next, we make the change of variable y(t) = T(t) - 20 (note that y(t) is nonnegative in the context of this problem and that y(t) is positive for finite values of t). Then we have that
y'(t) = \frac{d}{dt}[T(t) - 20] = T'(t)
\frac{dy}{dt} = -ky
y(0) = T(0) - 20 = 68 - 20 = 48
Use of the separation of variables method on this differential equation involving y gives us
\frac{1}{y}dy = -k dt (valid since y ≠ 0 for finite values of t)
⇒ ln|y| = -kt + C
⇒ |y| = e^{-kt + C}
⇒ y = e^{C}e^{-kt} (since y is positive for finite values of t)
⇒ y(t) = Ae^{-kt} (where A = e^{C})
The initial condition y(0) = 48 then gives us
y(0) = Ae^{-k*0}
= A*e^{0}
= A*1
= A
⇒ A = 48
⇒ y(t) = 48e^{-kt}
Since we are also given that T(5) = 25, we know that y(5) = T(5) - 20 = 25 - 20 = 5. Further, we can also conclude that
y(5) = 48e^{-k*5}
= 48e^{-5k}
= 5
⇒ 48e^{-5k} = 5
⇒ e^{-5k} = \frac{5}{48}
⇒ -5k = ln(\frac{5}{48})
⇒ k = \frac{1}{-5}ln(\frac{5}{48})
= \frac{1}{5}ln((\frac{5}{48})^{-1})
= \frac{1}{5}ln(\frac{48}{5})
≅ 0.4524
⇒ y(t) = 48e^{-[\frac{1}{5}ln(\frac{48}{5})]t}
≅ 48e^{-0.4524t}
⇒ T(t) - 20 = 48e^{-[\frac{1}{5}ln(\frac{48}{5})]t}
≅ 48e^{-0.4524t}
⇒ T(t) = 20 + 48e^{-[\frac{1}{5}ln(\frac{48}{5})]t}
≅ 20 + 48e^{-0.4524t}
Letting T(t) = 21, we finally have that
20 + 48e^{-0.4524t} = 21
⇒ 48e^{-0.4524t} = 21 - 20 = 1
⇒ e^{-0.4524t} = \frac{1}{48}
⇒ -0.4524t = ln(\frac{1}{48})
⇒ t = \frac{1}{-0.4524}ln(\frac{1}{48})
= \frac{1}{0.4524}ln((\frac{1}{48})^{-1})
= \frac{1}{0.4524}ln(48)
= 8.557031412
≅ 9
Thus, the roast will take 9 hours to cool down to 21 degrees Fahrenheit and the answer is B.


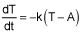 , where T is the water temperature, A is the room temperature, and k is a positive constant.
, where T is the water temperature, A is the room temperature, and k is a positive constant.



