Karime R.
asked • 09/13/22Find f + g, f − g, fg, and f/g and their domains.
f(x) = 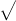
|
4 − x2 |
, g(x) = 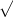
|
x + 1 |
1 Expert Answer
Raymond B. answered • 09/13/22
Math, microeconomics or criminal justice
for the domains eliminate any x values that make what's under the radical negative
domain is all other x values
that works for sum, difference and product of f(x) and g(x)
for the quotient (f/g)(x) also eliminate x=-1 as it makes the denominator =0 which is not allowed as division by zero is undefined
for range, y can't be negative, for sum, product or quotient
but it can be for the difference, (f-g)(x)
that's the goal, with luck maybe the following is correct. no guarantees. but double your money back, if you didn't pay anything. check x or y values outside the following domains and ranges and see if they work or not. You might get a headache thinking them through too much, though. sometimes it helps to work on these once, then put it aside a while, come back and work them again if you get the same answers, you increase your odds of being right. be careful on the endpoints. check them, as well as slightly more and less than those x values
(f+g)(x) = sqr(4-x^2)+ sqr(x+1)
domain is [-1,2]
as x<-2,x<-1, and x>2 make the square roots imaginary
range is [0, infinity)
(f-g)(x) = sqr(4-x^2)- sqr(x+1)
domain is the same
range is all real numbers
(fg)(x) = sqr((4-x^2)(x+1)) = sqr(-x^3-x^2+4x-4)
domain is same but also x< -2, (-infinity, -2]U[-1,2]
either 4-x^2 and x+1 are both negative or both are positive or one is zero. they can't be opposite signs
range is [0, infinity)
(f/g)(x)= sqr((4-x^2)/(x+1))
domain is (-infinity,-2]U(-1,2], unlike domain for (fg)(x), x=-1 is not in the domain so open parentheses, not closed for the -1 end point
range is [0, infinity)
range is all real numbers
Still looking for help? Get the right answer, fast.
Get a free answer to a quick problem.
Most questions answered within 4 hours.
OR
Choose an expert and meet online. No packages or subscriptions, pay only for the time you need.





Karime R.
Find (f + g)(x). Find the domain of (f + g)(x). (Enter your answer using interval notation.) Find (f − g)(x). Find the domain of (f − g)(x). (Enter your answer using interval notation.) Find (fg)(x). Find the domain of (fg)(x). (Enter your answer using interval notation.) Find f g (x). Find the domain of f g (x). (Enter your answer using interval notation.)09/13/22