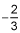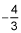Recall that the Maclaurin expansion for a function is the Taylor series centered on x0 = 0.
So, in general, f(x) ~ ∑n=0∞ f(n)(0)·xn/n! where f(n)(x) is the nth derivative.
So the cubic coefficient would be f"'(0) / 3!.
f(x) = sin2x
f'(x) = 2cos2x
f"(x) = -4sin2x
f"'(x) = -8cos2x
f"'(0) = -8 and the coefficient of x3 in the expansion is - 4/3.